BRIX
Mobile robotic system for autonomous bricklaying on unstructured construction sites
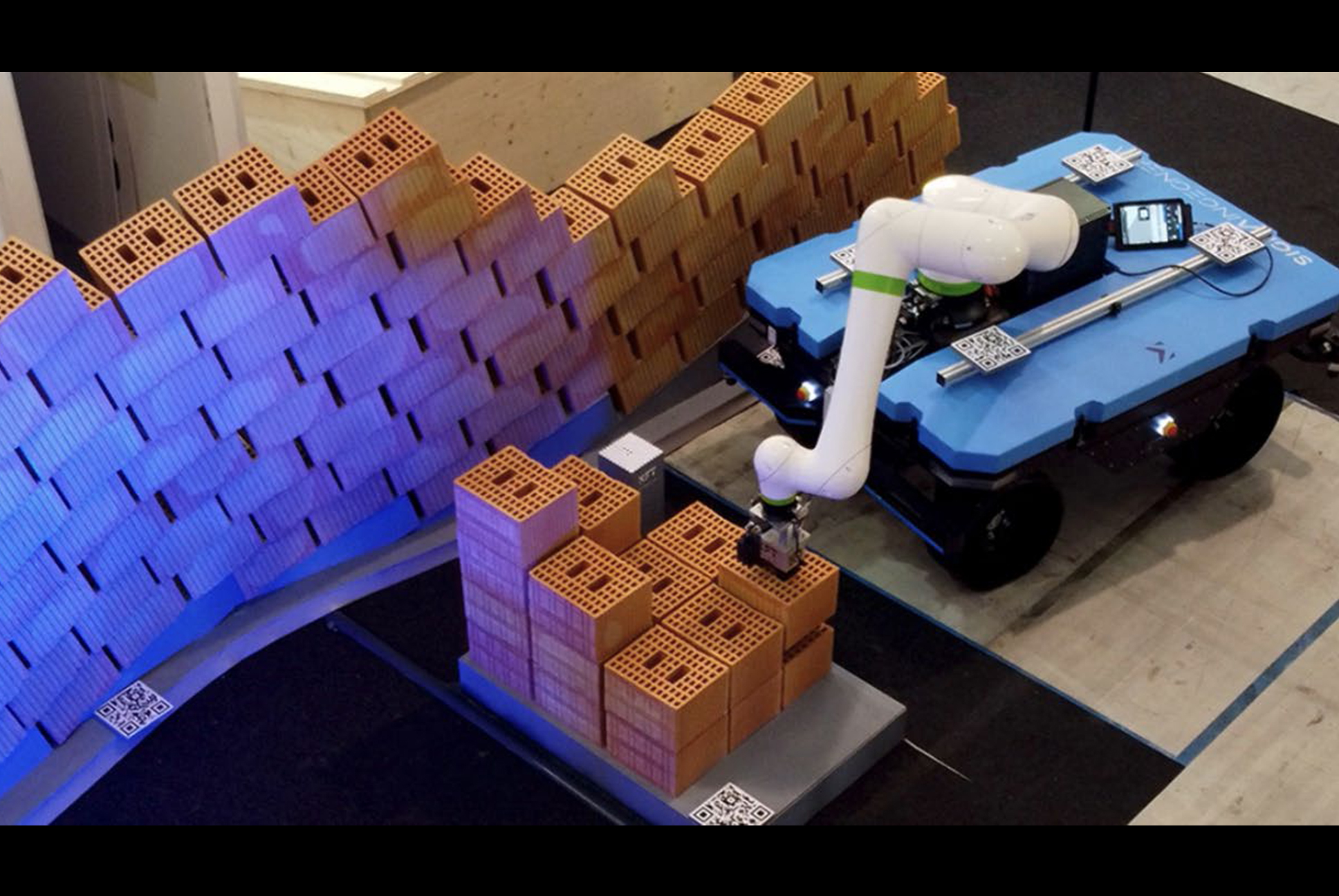
BRIX is a mobile robotic system designed to automate bricklaying tasks on active construction sites. Combining a lightweight autonomous rover with a robotic arm, the system addresses the challenges of navigating unstructured environments while performing material placement with minimal human intervention. Through sensor fusion and real-time localization, BRIX operates without pre-mapped environments and adapts to site conditions. A full-scale demonstrator validated the system’s ability to assemble freeform brick structures under non-ideal terrain conditions, highlighting its potential to streamline on-site fabrication workflows.
Most robotic construction systems are limited by weight, size, and the need for pre-mapped environments, restricting their use on dynamic, uneven sites. BRIX proposes a mobile, lightweight alternative capable of autonomous navigation and material placement without prior site preparation.
The project targets bricklaying tasks, focusing on maintaining placement accuracy under unpredictable conditions. Challenges include real-time localization on rough terrain, reliable gripping without fixed guides, and integrating navigation, manipulation, and user control into a continuous workflow, minimizing external infrastructure and increasing adaptability.
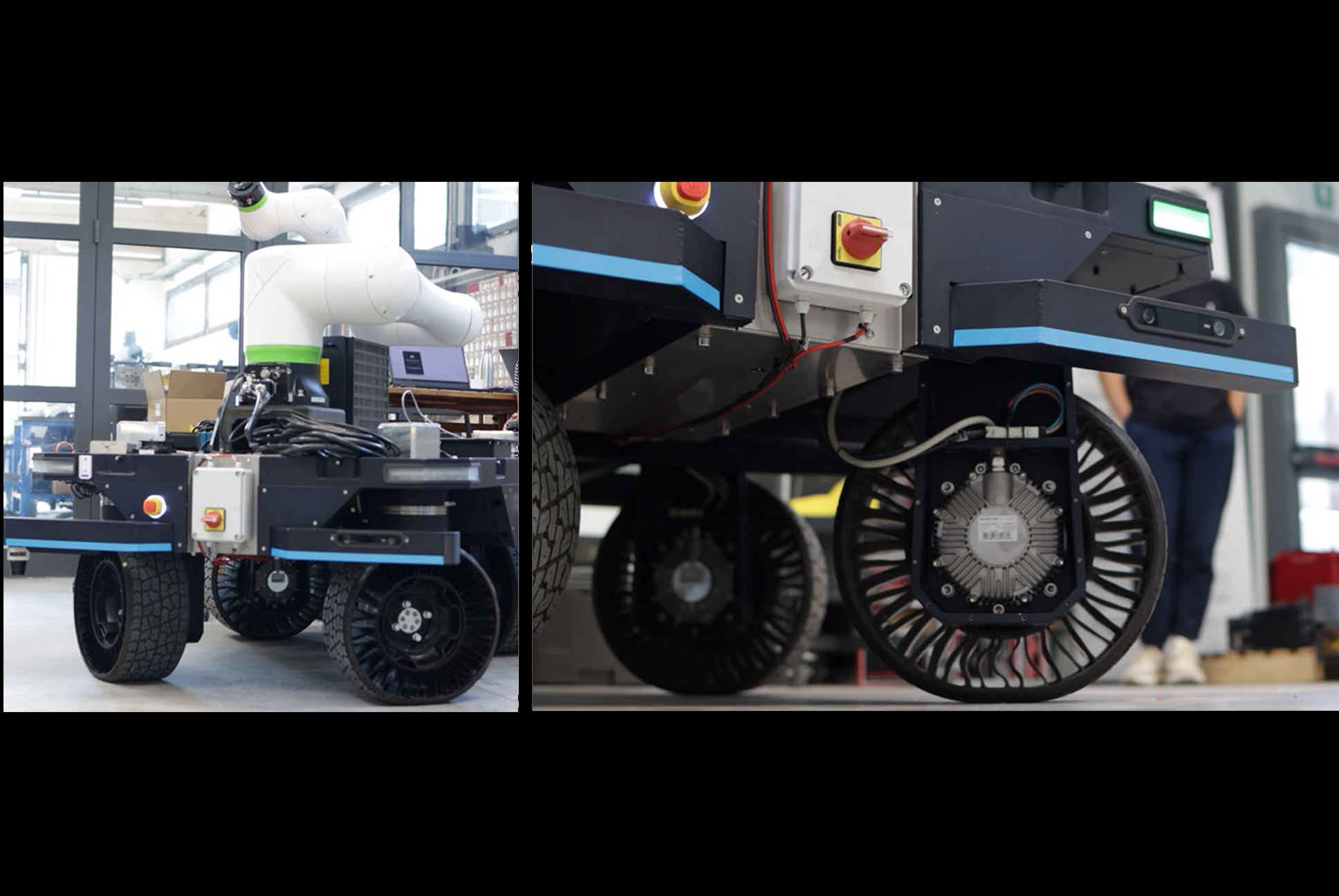
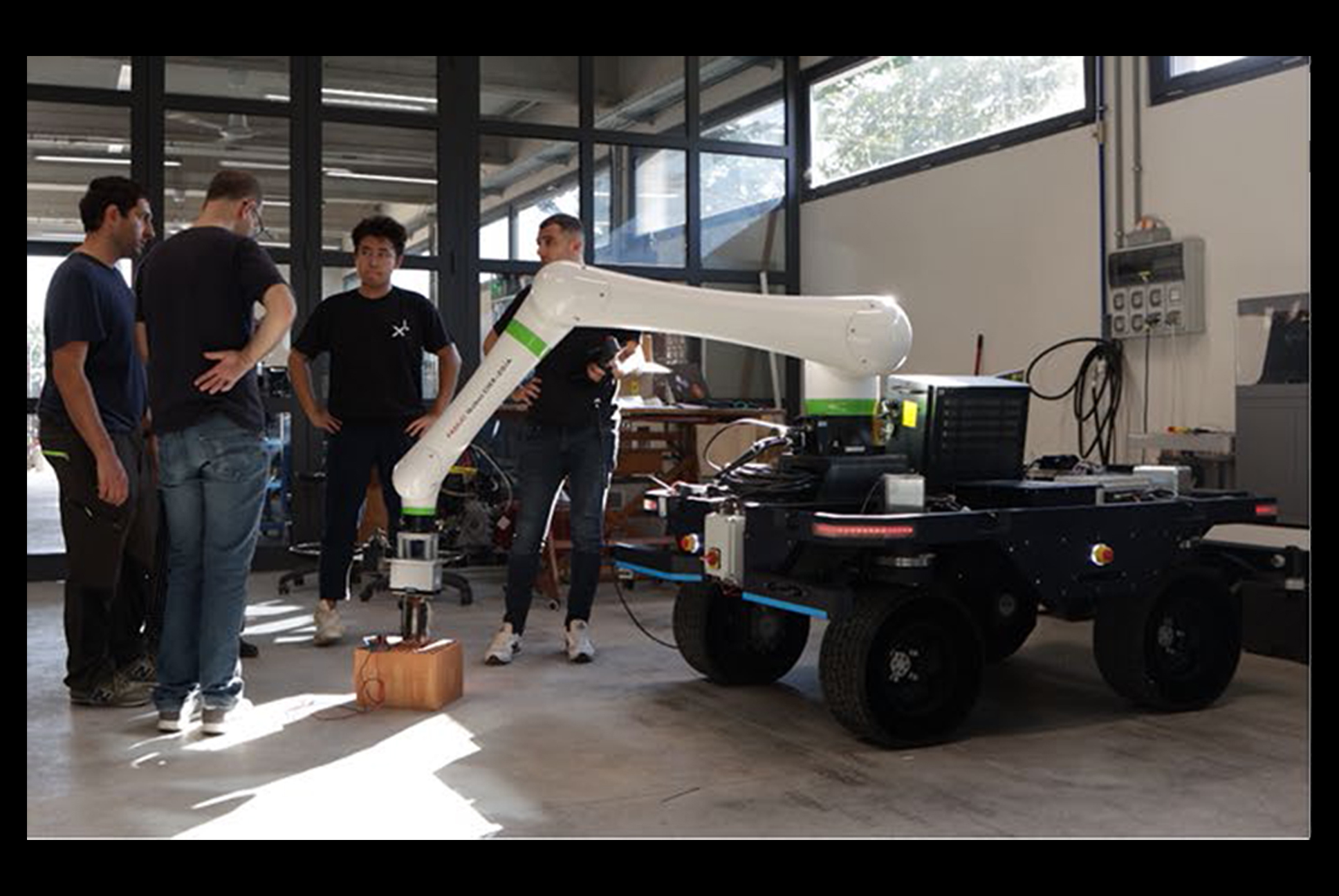
The system consists of a mobile platform equipped with a collaborative robotic arm, a custom-designed brick gripper, and a multi-sensor localization system. The rover navigates using a combination of LiDAR, stereo cameras, GPS, and wheel encoders, enabling real-time positioning without pre-installed markers or maps.
BRIX operates through a multi-layered control framework. The localization layer fuses sensor data to estimate the robot’s position and correct drift. A high-level planning layer assigns waypoints and tasks based on a virtual representation of the structure to be built. The manipulation layer manages the robotic arm’s movements for brick picking, transport, and placement, while compensating for terrain variations through online correction.
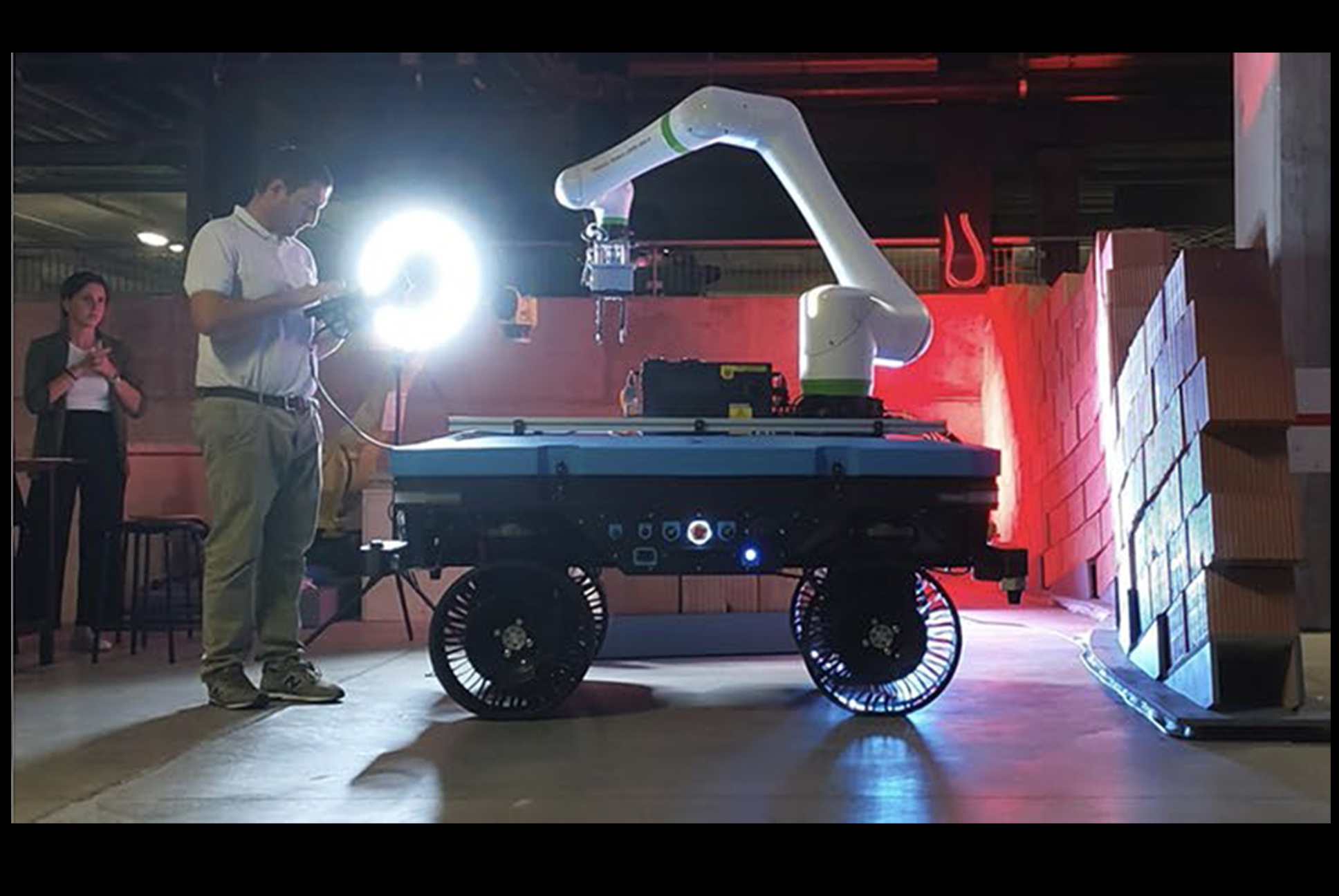
The gripping device secures bricks with positional tolerances, reducing the need for high-precision fixtures. Augmented reality is used to define safety zones and assist workers in monitoring progress, supporting human-robot collaboration without interrupting operations. A user interface allows non-expert control of task execution and system supervision.
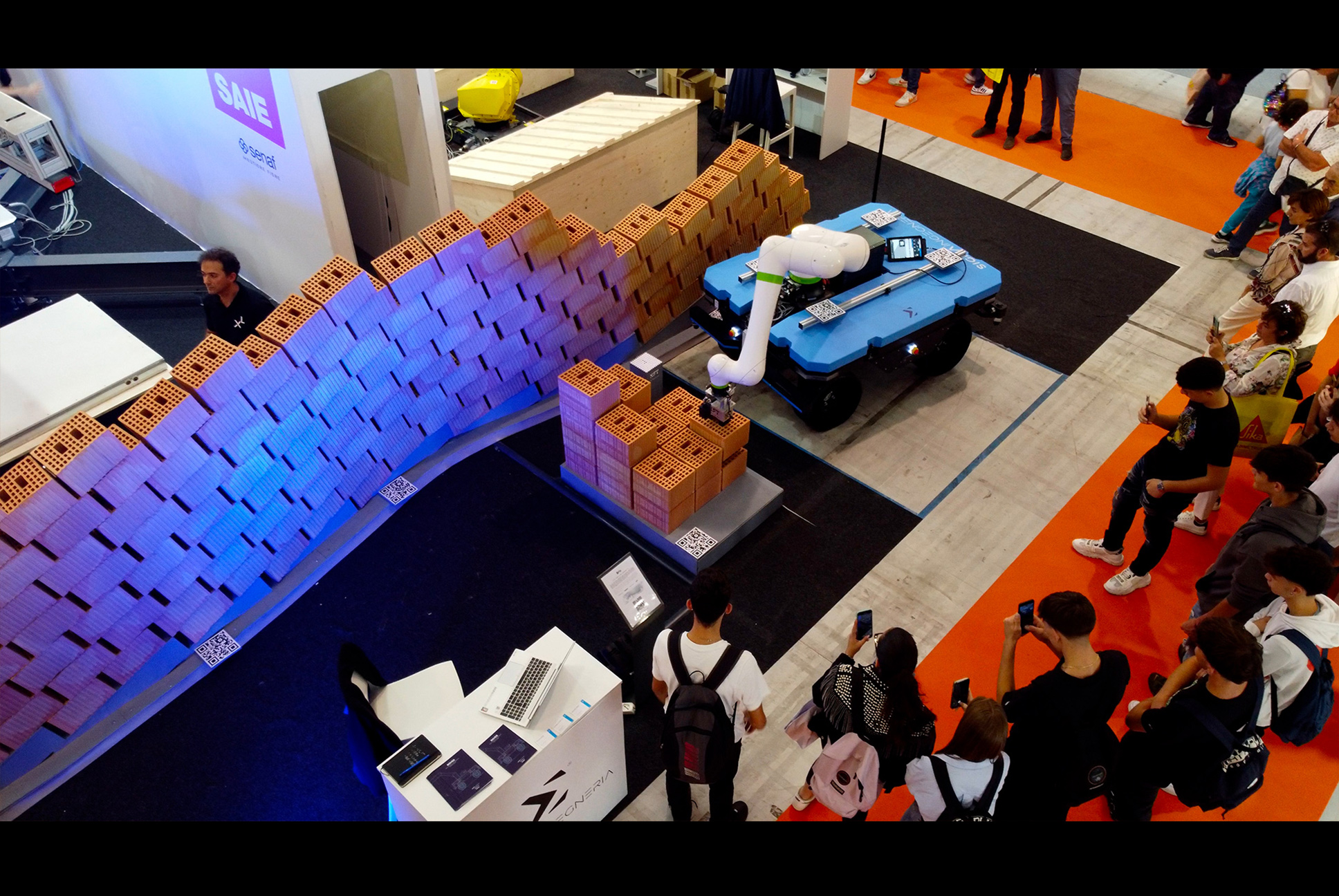
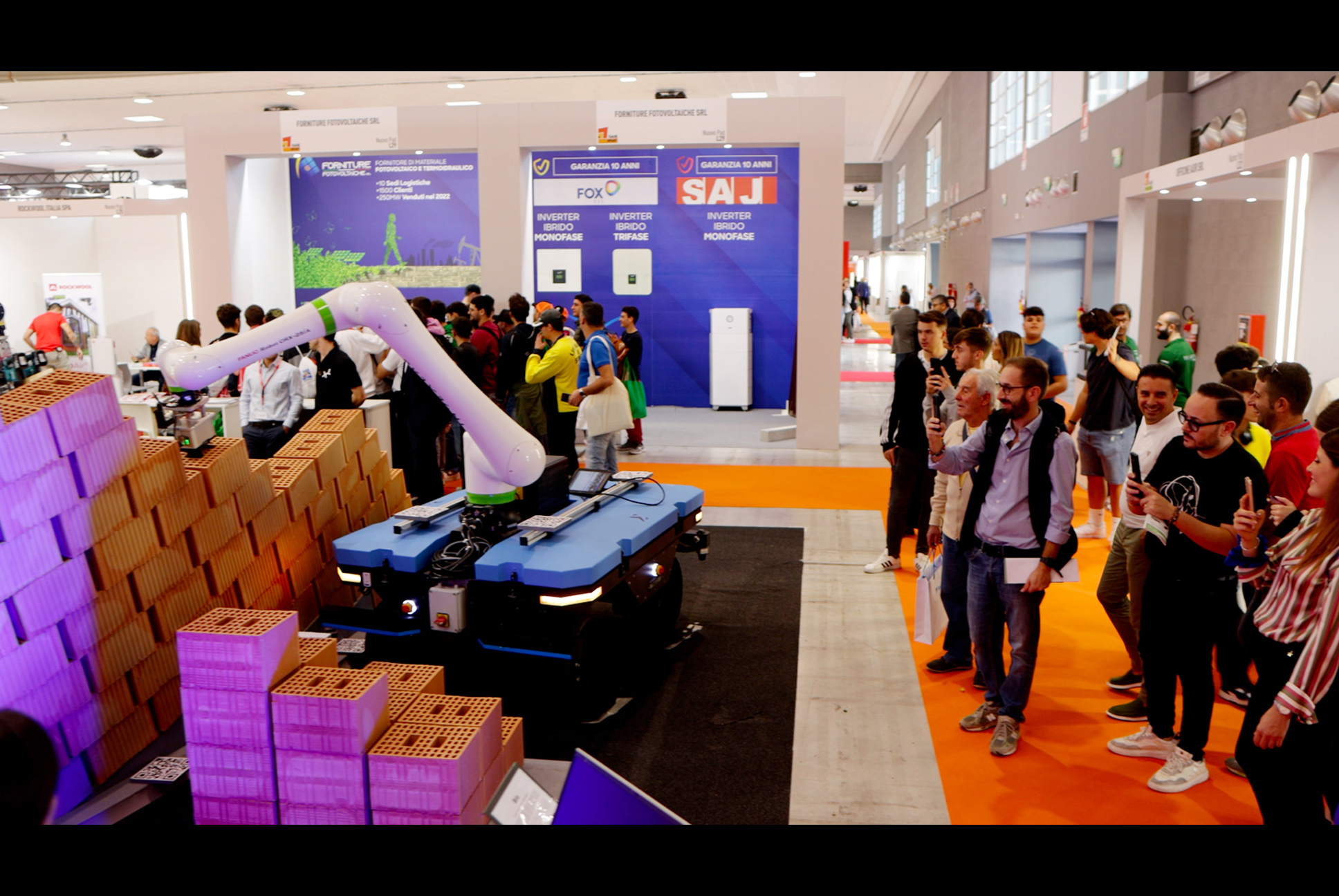
At SAIE 2023, BRIX autonomously built a freeform brick wall. The system maintained reliable localization without prior mapping, placed bricks within acceptable tolerances despite minor ground irregularities, and enabled safe human supervision through augmented reality-defined safety zones. The demonstration confirmed the system’s ability to adapt to site variability and execute autonomous material placement under real-world conditions.
space
MATERIALS
Bricks | Digital Materials
PROCESSES
Robotic Tiling and Bricklaying | Vision Systems | Autonomous Construction Equipment | Augmented Reality
DESIGNS
Parallel Sectioning | Discrete Part-Based Modularity
space
ROLES
.
STAKEHOLDERS
LOCATION
First exhibited at SAIE Fair in Bari, Italy
YEAR
2023
space